Intriguing research based on 450,000 Britons has found that youngsters born in the summer months are stronger and taller.
It is though that during spring and summer pregnant mothers absorb more of health-boosting Vitamin D from sunshine in the second and third trimesters, giving their offspring a head-start.
Vitamin D is important for maintaining healthy bones and is thought to protect against cancer, type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis.
The study also revealed that girls born in the summer started puberty later, an indication of better health in adult life. Early developers are at increased risk of heart disease and diabetes.
So, according to the University of Cambridge study, prospective parents have a three month window in the autumn to ensure their babies have the best start in life.
"When you were conceived and born occurs largely `at random` - it`s not affected by social class, your parents` ages or their health - so looking for patterns with birth month is a powerful study design to identify influences of the environment before birth," said Dr John Perry, lead author of the study.
"We were surprised, and pleased, to see how similar the patterns were on birth weight and puberty timing.
“Our results show that birth month has a measurable effect on development and health, but more work is needed to understand the mechanisms behind this effect."
The researchers compared the growth and development of around 450,000 men and women from the UK Biobank study, to find out whether the environment in the wombs lead to changes that can influence health in later life.
This effect, called programming, is known to have consequences for development throughout childhood and into adulthood.
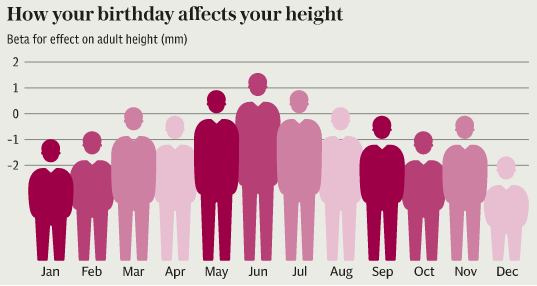
They found that children born in June, July, and August were heavier at birth and taller as adults. Summer babies were 10 per cent less likely to be of short stature - under 5ft 9 inches for men and 5ft 3 inches for women. It means the average Briton born in December will be, on average, three millimetres smaller than someone born in June.
The researchers believe that the differences between babies born in the summer and the winter months could be down to how much sunlight the mother gets during pregnancy, since that in part determines her vitamin D exposure.
"We don`t know the mechanisms that cause these season of birth patterns on birth weight, height, and puberty timing," said Dr. Perry.
"We need to understand these mechanisms before our findings can be translated into health benefits.
“We think that vitamin D exposure is important and our findings will hopefully encourage other research on the long-term effects of early life vitamin D on puberty timing and health."
However the authors point out that all of the people involved in the study were born in Britain before Vitamin D supplements were recommended for pregnant mothers, so a study on babies born today may show different results.
The study also picked up variations in educational achievement based on month of birth with academic success rising sharply in the autumn, believed to be caused by the difference in ages of the school year. Children born in August can be nearly a year younger than their classmates.
“This leads to variation in physical and academic performance within each school year,” the authors conclude.
Previous studies have found that people born in November are far less likely to develop Multiple Sclerosis than those born in May, which has again been linked to vitamin D.
Research has also shown that children grow more quickly in spring and summer, and more slowly in autumn and winter.
The study found no link between month of birth and body mass index (BMI).
More about:
















































