Almost complete regeneration every decade
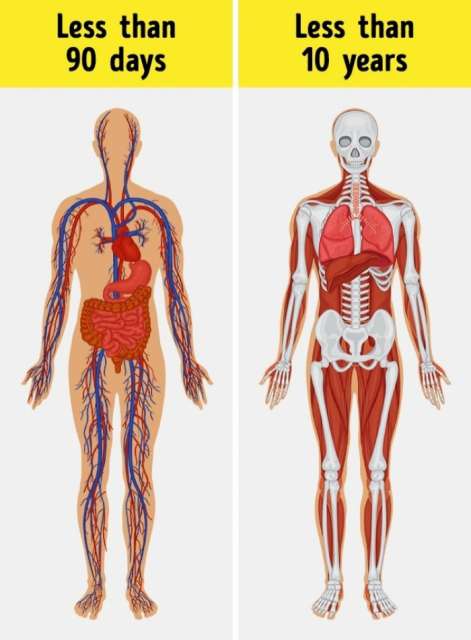
Every day, about 70 billion cells die in our body, and we don’t even notice. A new intestinal tract appears every 3-4 days; red blood cells die every 3 months; the kidney cells renew themselves over a year. Within a decade, our body undergoes an almost complete regeneration. Some cells live more than a century, though, such as neurons.
Every navel is a universe of bacteria
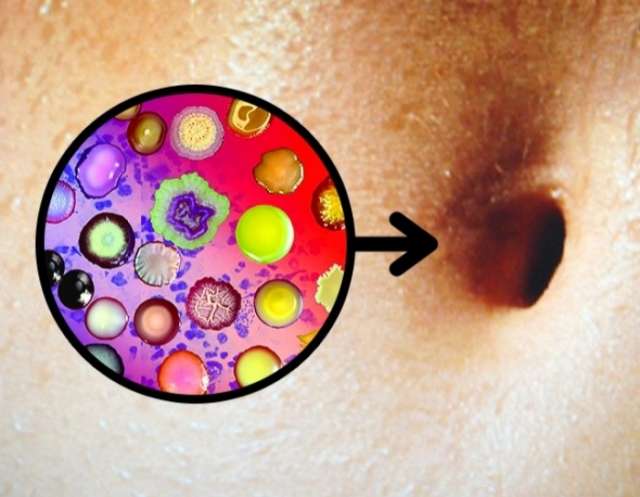
It sounds creepy, but there are thousands of bacteria in every navel, and they create their own ecosystem. Scientists say it looks a lot like a rainforest: the flora is at a balance, and certain types of bacteria are dominant. Each navel has its own set of bacteria and its own ecosystem.
Taste receptors are located in the heart
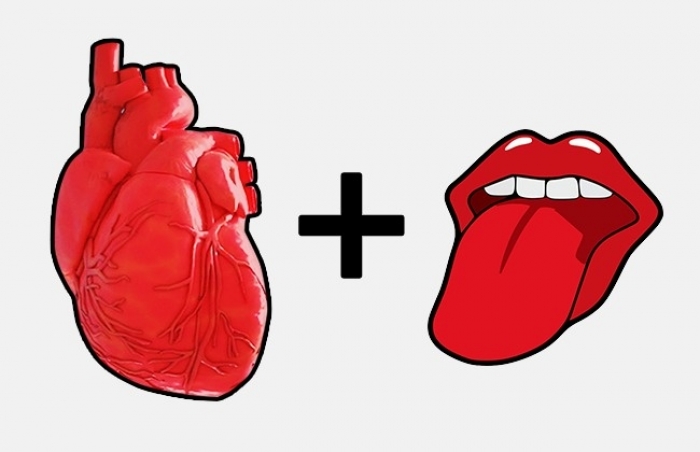
Babies have so many taste buds that some of them are situated on the palate, but they disappear with age. Adults have about 10,000 receptors in their mouth — a number that is cut in half by the age of 60. However, it’s recently been found that receptors of sourness are also located in the heart to help it recognize infections.
Stomach acid can dissolve iron
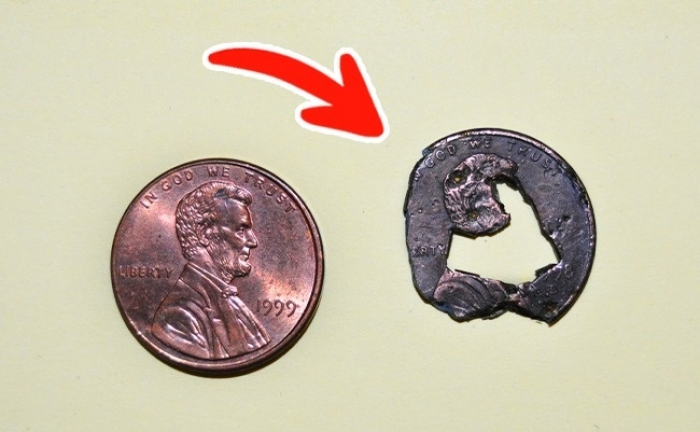

Our stomach contains hydrochloric acid. Having heated the stomach acid up to 37°С, scientists placed iron blades and an alkaline battery in it. After 24 hours, the blade lost 63% of its mass, while the battery withstood the assault for more than a day. To sustain such loads, our body has to produce new gastric cells before the acid destroys the old ones.
Emotions create false memories
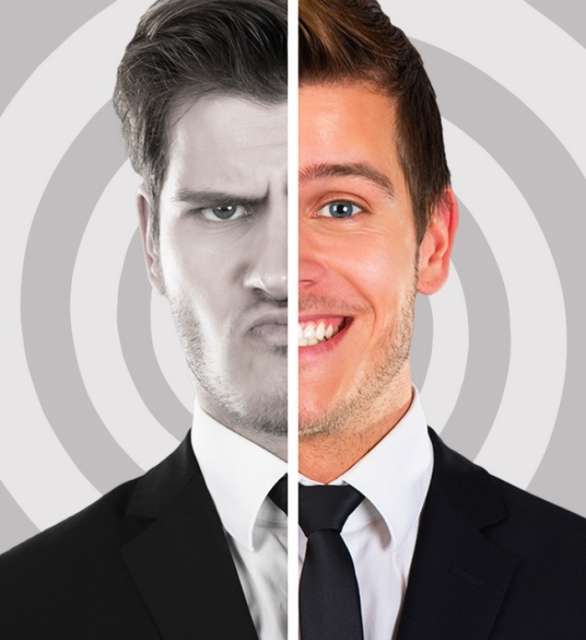

If you trust your memory, we’ve got bad news for you. Our memories change every day depending on our current emotional state. For instance, you went on a great trip with your best friend last year, but some time ago you argued and stopped seeing each other. Now, recalling the trip, you’ll feel it wasn’t that great after all: your brain will find (or even make up) something bad about it so you don’t enjoy these memories or come back to them.
The contents of milk adjust for the baby

Breast milk contains hundreds of useful substances that help a baby grow and develop immunity. It’s recently been discovered that milk actually changes its contents and consistency to adjust for a baby during feeding. The mother’s body analyzes the baby’s saliva to give it the "cocktail" it needs, changing it on the go.
We are taller and slimmer in the morning
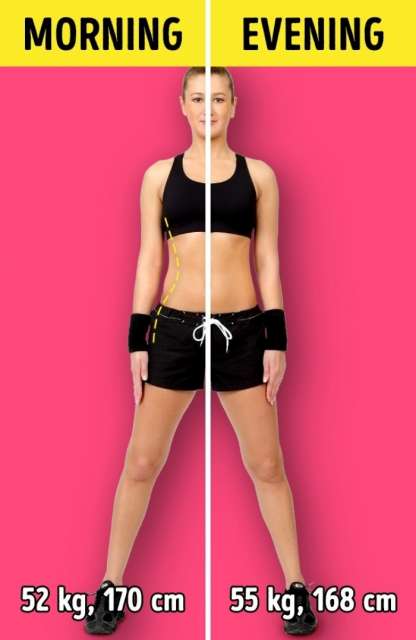

It’s common knowledge that the intervertebral discs aren’t as firmly adjoined to one another when we’re asleep as when we’re awake, and by morning a person becomes 1-2 cm taller. Many will also notice that we don’t weigh as much. At night, our body continues to work to get rid of excess liquid and air, and through breathing and sweating we lose up to 2 kg per night.
When you flush, your stomach does too
Scientists recently claimed that the way to a woman’s heart is also through her stomach. We get kinder when we’re satiated; we feel butterflies in our stomach when we’re in love; and when a person flushes with embarrassment, their gastric mucus also turns red.
Everyone has UV vision
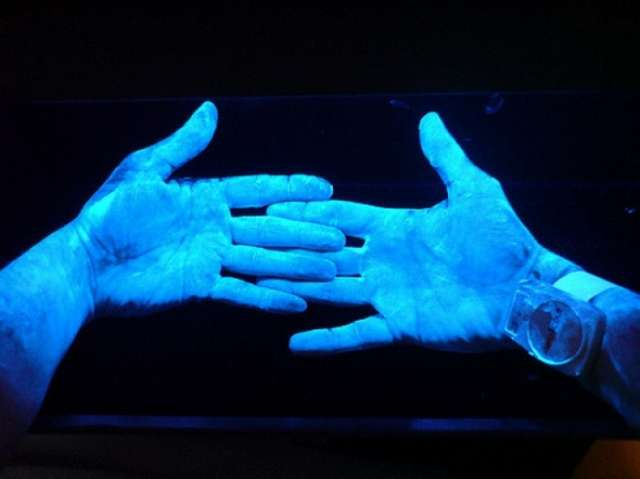

The treatment of cataracts includes removal of the eye lens, returning UV sight to many patients (that’s exactly what happened to Claude Monet). We don’t need this ability in usual circumstances, and nature created the eye lens that protects our eyes from UV rays. Among mammals, reindeer have UV vision that helps them discern the fur of white polar predators and edible lichen on the snow.
Half of our body consists of bacteria
It was not long ago assumed that there were 10 times more bacteria in our body than our own cells, but recent studies disproved this assumption: the body of an adult human is home to 30-40 trillion bacteria, roughly equal to the number of our own cells. The highest bacterial density is in the rectum, and that’s why each defecation makes our own cells win over the bacteria.
If your eyes mix complementary colors, you see white
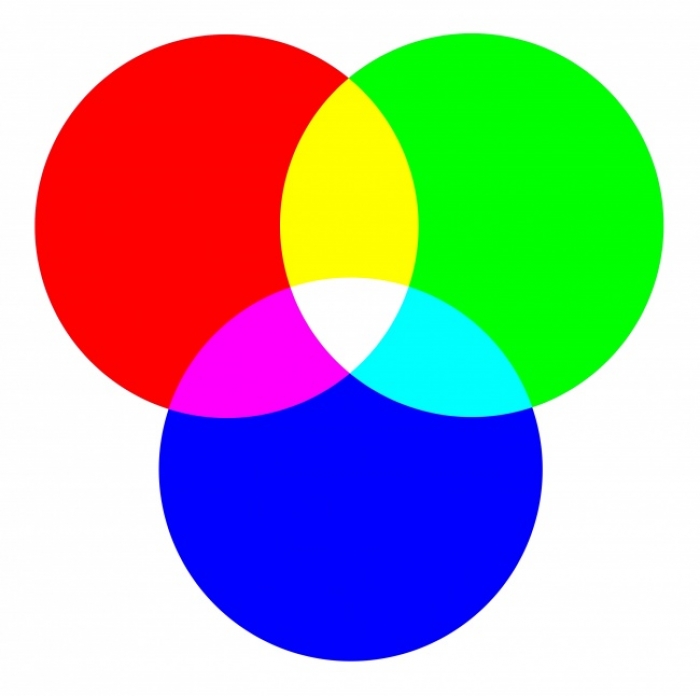
Don’t confuse complementary colors on a paint color wheel with those on a light color wheel. In the first case, if you mix two opposite colors you’ll get something brownish, as adding more pigments signifies that more colors are absorbed. A light color wheel is a different story: your eyes perceive them in combination, so you get white. The following video illustrates how it works. The red screen and the cyan screen are switched back and forth quickly, and you seem to see white between the shots. However, if you pause the video you’ll find the screen to be either red or cyan (this may not work on mobile devices).
More about: #body

















-1740752813.jpg&h=190&w=280&zc=1&q=100)





























